Navigating the world of taxes can often feel complex, but it doesn’t have to be. In Pakistan, the central body responsible for managing the country’s taxation system is the Federal Board of Revenue of Pakistan. This organization plays a crucial role in the nation’s economy by collecting revenue and implementing fiscal policies. Understanding its functions is the first step for any citizen or business owner toward better financial planning and compliance. This guide offers a clear look into how the FBR operates, its responsibilities, and how you can interact with it effectively.
Mandate and Core Functions
The FBR operates under the FBR Act, 2007, and serves as Pakistan’s primary revenue collection agency. Its mandate is broad, covering the administration and enforcement of laws related to a wide range of taxes. The core purpose is to collect federal taxes and duties efficiently. Its functions include formulating tax policy, ensuring taxpayer compliance, and preventing tax evasion. By managing revenue collection, the FBR directly contributes to the national budget, funding public services like infrastructure, healthcare, and education for the country’s citizens.
Organizational Structure
To manage its diverse responsibilities, the organization is divided into various wings and directorates, each specializing in a specific area of taxation. Key divisions include Inland Revenue and Pakistan Customs. The Inland Revenue Service is responsible for domestic taxes such as income tax, sales tax on services, and federal excise duty. On the other hand, Pakistan Customs manages taxes on goods entering or leaving the country, including customs duties. The chairman leads the Federal Board of Revenue of Pakistan, and members support him by overseeing different operational areas to ensure a structured approach to revenue administration.
Key Taxes Administered
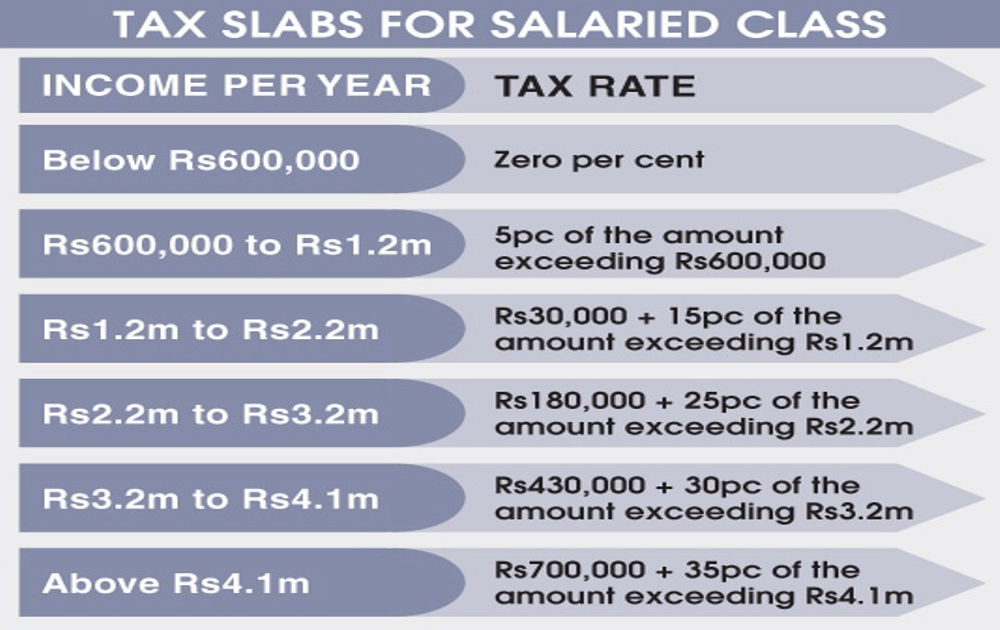
The FBR administers several major federal taxes that impact individuals and businesses across the country. The most significant of these is the Income Tax, which is levied on the income of individuals, associations of persons, and companies. The government applies the Sales Tax as an indirect tax on the sale of goods. It also imposes Federal Excise Duty (FED) on specific goods manufactured or imported into Pakistan, as well as on certain services. Lastly, authorities charge Customs Duty on imported goods to regulate trade and protect local industries. Understanding these different taxes is essential for proper compliance and financial management.
Digital Transformation and e-Filing
In recent years, the FBR has made significant strides in modernizing its processes through digital transformation. A major part of this effort is the introduction of an online taxpayer portal, known as Iris for income tax and WeBOC for customs. These platforms have streamlined the process of filing tax returns, making it easier for taxpayers to meet their obligations from anywhere. The move toward e-filing has reduced paperwork, increased transparency, and improved the efficiency of the taxation system. Digital payments for taxes have also been introduced, simplifying the process of settling liabilities.
Compliance, Audits, and Enforcement
Ensuring compliance is a fundamental task of the tax authority. The organization employs various measures to encourage voluntary compliance, but it also has robust mechanisms for enforcement. This includes conducting audits to verify the accuracy of tax returns. The Federal Board of Revenue of Pakistan often uses a risk-based selection process to choose which cases to audit, focusing on returns that show a higher probability of error or evasion. When non-compliance is detected, the FBR has the authority to enforce tax laws through penalties, recovery of unpaid taxes, and other legal actions. Keeping proper documentation is a taxpayer’s best defense during an audit.
Taxpayer Services and Education
Recognizing that an informed taxpayer is more likely to be a compliant one, the FBR has expanded its taxpayer services and education initiatives. It provides information through its official website, public notices, and media campaigns. These resources help explain tax laws, filing procedures, and important deadlines. The organization also operates help centers and call centers to answer queries and provide assistance. These services aim to make the tax system more accessible and user-friendly, guiding citizens and businesses through their responsibilities and helping them resolve issues like securing refunds or understanding withholding tax rules.
Economic Impact and Policy Role
Beyond revenue collection, the FBR plays a vital role in shaping Pakistan’s economic landscape. The data it collects provides valuable insights into economic trends, which inform national fiscal policy. The board advises the government on tax-related matters, contributing to the annual federal budget. By adjusting tax rates, offering incentives for specific sectors, or implementing trade policies through customs duties, the FBR influences investment, consumption, and overall economic growth. Its actions have a direct impact on the country’s financial stability and development agenda.
Challenges, Reforms, and the Road Ahead
The FBR faces several ongoing challenges, including a narrow tax base, a large informal economy, and issues with tax evasion. To address these, the organization is continuously pursuing reforms. These initiatives focus on broadening the tax net, simplifying tax laws, and leveraging technology to improve transparency and efficiency. The goal is to create a more equitable and effective taxation system that supports sustainable economic growth. The road ahead involves further modernizing processes, enhancing data analytics for enforcement, and building greater trust between taxpayers and the administration.
Conclusion
The Federal Board of Revenue of Pakistan is the backbone of the country’s financial system, responsible for everything from tax collection and policy formulation to enforcement and taxpayer education. Its work in administering income tax, sales tax, and customs duties directly funds public services. Through digital initiatives like e-filing, it is making compliance easier. While challenges remain, its ongoing reforms aim to build a more efficient and transparent taxation system for the future.
FAQs
- What is the main function of the FBR?
The FBR’s primary function is to collect federal taxes in Pakistan, including income tax, sales tax, federal excise duty, and customs duty, to generate revenue for the government. - How can I file my tax return online?
You can file your income tax return online through the FBR’s Iris portal. You need to register for an account, fill out the relevant forms with your income and tax details, and submit it before the filing deadline. - What is the difference between Inland Revenue and Customs?
Inland Revenue is the arm of the FBR that deals with domestic taxes like income tax and sales tax on services. Pakistan Customs is responsible for managing taxes on goods imported into or exported from the country. - What happens if I am selected for a tax audit?
If selected for an audit, the FBR will review your financial records and tax returns to verify their accuracy. You will be required to provide supporting documentation for your income and expenses. It is important to cooperate and provide clear records. - How can I pay my taxes?
You can pay your taxes through designated banks, online banking platforms, or alternative delivery channels (ADCs) like ATMs. You need to generate a Payment Slip ID (PSID) from the FBR’s system to make the payment.